(L209) Blanks 2 Bundle: Language Comprehension Booster – Classification Tasks
Original price was: $47.92.$43.00Current price is: $43.00. including GST
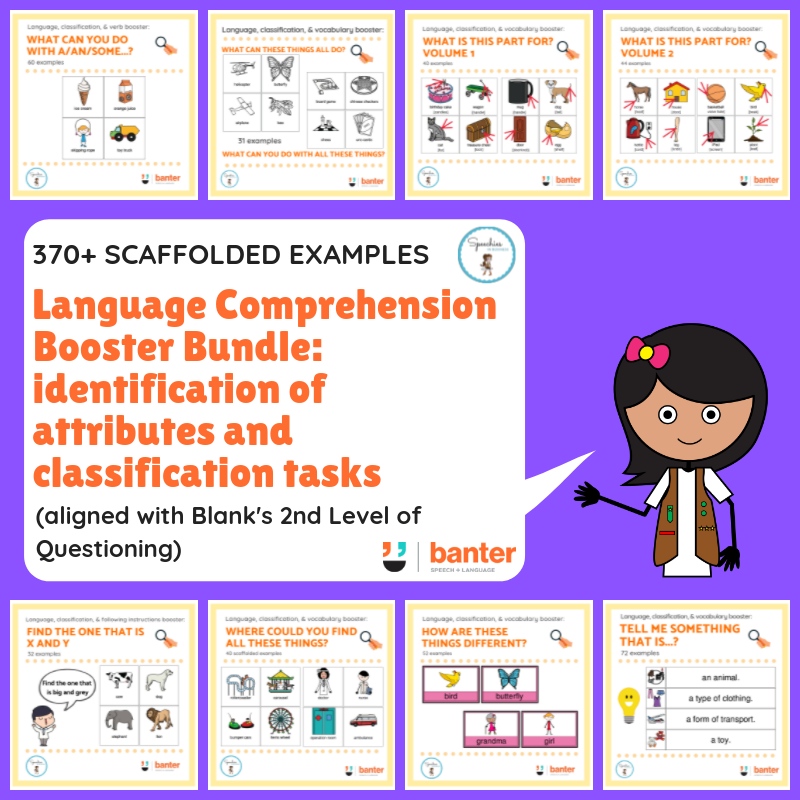
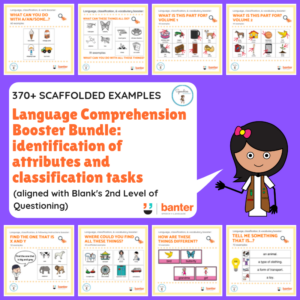
In this no-prep bundle of resources (240 pages), we target Blank’s Level 2 language comprehension tasks, which requires the student to identify attributes of objects and to categorise them. Specifically, this bundle includes:
Description
Some researchers think that up to 15% of young school kids don’t have the language comprehension skills to cope fully with the demands of school (Hart & Fielding-Barnsley, 2009). Many of these kids struggle – some for their whole lives. For most kids, school and home life plays a big role in helping to understand and use language (Morgan & Goldstein, 2004; Nation, 2005). So what can we do to improve students’ understanding of language
Well, it helps to have a plan. And good plans are based on tried and tested frameworks. For language comprehension, one of the most influential frameworks was developed by Dr Marion Blank, a developmental psychologist. Dr Blank proposed four levels of abstraction, from least to most abstract:
- Level 1: Directly supplied information (Matching perception)
- Level 2: Classification.
- Level 3: Reorganisation.
- Level 4: Abstraction and Inferences.
Not all kids start school with an ability to complete Level 2 tasks, which relate to classification and categorisation. Broadly speaking, humans have two mains ways of organising information:
- Categorisation: dividing the world into groups of entities whose members are similar to each other in some way.
- Classification: systematically assigning each object or entity to one – and only one! – class within a system of mutually exclusive, non-overlapping classes.
For typically developing children, categorisation begins in infancy, starting with categorising objects according to basic concepts (e.g. colour and shape). Early categorisation may be purely perceptual (e.g. “these objects look alike”, or “all these things have four legs”), meaning that the child doesn’t necessarily understand the logical relationships among the grouped objects.
Typically developing preschoolers:
- first compare objects, abstracting similarities and differences between objects (e.g. looking at a glass and a mug, noting that we drink from both, but a glass is see-through, and a mug is not); and
- then categorise them – i.e. put them in groups according to “essential” or relevant similarities (e.g. “cups and mugs are things we drink from”).
We can categorise things in several ways, e.g. by function (what we do with things, or what they do), parts, by group (e.g. alive/not alive, animals, transport, etc.), by parts, materials/what things are made of, origin, location and of course basic perceptual characteristics like size, colour, scent, texture – almost any attribute you can imagine.
The developmental sequence is:
- comparison; then
- categorisation; then
- conceptualisation; and finally,
- classification.
In this bundle of resources, we target Blank’s Level 2 language comprehension tasks, which requires the student to identify attributes of objects and to categorise them. Specifically, this bundle includes:
- What can you do with a… (Functions)
- What can these things all do/what can you do with these things? (Grouping by function)
- What is this part for? Volume 1
- What is this part for? Volume 2
- Find the one that is X and Y (Multiple perceptual attributes)
- Where could you find all these things? (Locations)
- How are these things different? (Comparison)
- Tell me something that is a/an….? (Groups)
We have used these resources in our busy speech pathology clinic to support students with a range of different needs, including students with language and learning disorders, as well as students with Autism Spectrum Disorder. These resources are also appropriate for students of all ages who are learning English as an additional language.
For more Blank’s resources, our:
- Blank’s Level 3 language comprehension bundle is available here; and
- Blank’s Level 4 language comprehension bundle is available here.
For more information about categorisation and classification and their relationship to language development, check out our article here.